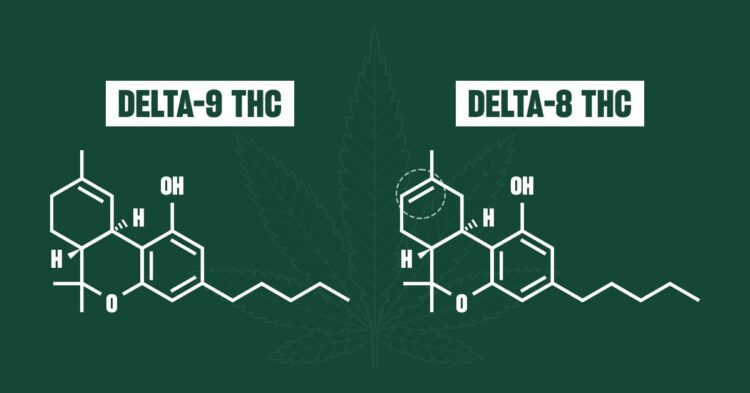
The broad spectrum of compounds found within the cannabis plant includes Delta-9 Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and Delta-8 THC. These two cannabinoids are particularly noteworthy due to their psychoactive properties and their contrasting legal status. This article aims to provide clarity on these differences, as well as advice for consumers navigating the ever-complex legal landscape of cannabis.
What is Delta-9 THC?
Delta-9 THC is the primary psychoactive component of cannabis and the compound that most people are referring to when they discuss the effects of marijuana. Delta-9 THC interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system to create the “high” associated with cannabis use, which can include feelings of euphoria, sensory enhancement, relaxation, and altered perception of time.
From a legal perspective, Delta-9 THC is a Schedule I drug under the federal Controlled Substances Act in the United States. This means it is illegal under federal law, although there is significant variation in state laws. Some states have legalized it for recreational and/or medical use, while others maintain its prohibition.
What is Delta-8 THC?
Delta-8 THC, on the other hand, is a lesser-known cannabinoid derived from hemp and occurs naturally in cannabis, although in much smaller amounts than Delta-9 THC. Like its more famous cousin, Delta-8 THC also interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system, but it tends to produce a more mild, clear-headed “high” with less anxiety and paranoia.
Despite its psychoactive properties, Delta-8 THC exists in a legal gray area. The 2018 Farm Bill in the United States legalized hemp and all of its derivatives, which would technically include Delta-8 THC. However, due to its psychoactive effects, it has come under increased scrutiny, and some states have moved to ban it.
Key Differences
Both Delta-8 and Delta-9 THC are chemically similar and interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system. However, their specific atomic structure varies, which leads to differing effects on the body. Delta-9 THC binds more readily with CB1 receptors in the brain, producing stronger psychoactive effects. Conversely, Delta-8 THC interacts with both CB1 and CB2 receptors, resulting in a milder, less intense experience.
Moreover, the legal differences are significant. As stated, Delta-9 THC is illegal under federal law and only legal in certain states. However, Delta-8 THC, due to its derivation from hemp, is technically legal at the federal level but is starting to be banned in some states.
What Does This Mean for Consumers?
As a consumer, it’s crucial to understand the differences between Delta-8 and Delta-9 THC, both in terms of their effects and their legality. In most states, if you’re purchasing from a licensed dispensary, you’re likely buying products containing Delta-9 THC.
Delta-8 THC is more commonly found in online stores and in states where marijuana is not legal for recreational use. However, given the shifting legal landscape, consumers should always double-check their state laws before purchasing Delta-8 THC products.
As always, responsible use is key. While Delta-8 THC may produce milder effects, it is still a psychoactive substance. Users should be aware of their personal tolerance levels and monitor their consumption accordingly.
Conclusion
Navigating the world of cannabis can be complex due to the variety of compounds, fluctuating legal statuses, and varying physiological effects. However, understanding the key differences between Delta-8 and Delta-9 THC can help consumers make informed decisions about their cannabis consumption.
As research continues to illuminate the multifaceted world of cannabis and its many compounds, consumers should stay informed about current laws and the scientific literature to ensure their cannabis use is safe, legal, and enjoyable.
CHECK THIS: Increased Enforcement of Delta 8 THC Across the U.S.
Physicians Advise Elderly People to Limit THC Intake